Give Classification of Organic Compounds With Example
What is organic compound?
Organic compound in chemistry is the class of chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen chemical bonding. Carbon has the property to combine with other carbon atoms to form a long chain. Therefore, it forms more than 3 million chemical compounds. From a common definition, organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon compounds or molecules. The definition includes compounds like carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbonates, and carbon disulfide, etc. These are the kingdom of inorganic series. In learning chemistry, the definition or classification of chemical compounds such as organic and inorganic compound is very complicated. Hydrocarbons (alkanes, alkenes, acetylene), aldehyde, ketone, alcohol, ether, carboxylic acid are the most common class of organic compounds.
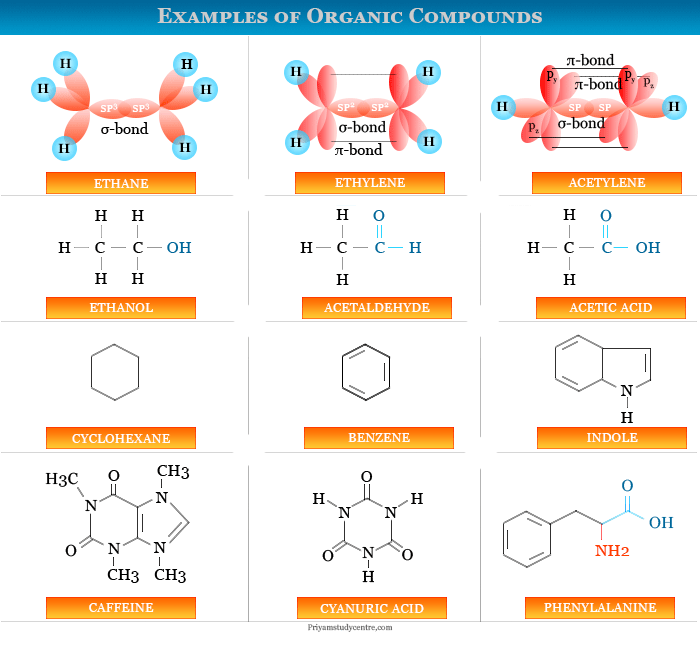
Types of organic compound
To differentiate different types of organic and inorganic molecules, the substances are classified into two groups.
- Substances that are prepared from green plants or animals (living world).
- Substances that are not prepared from the living world.
Pure organic compounds like sugar, starch, amino acids, enzymes, alcohol, resins, indigo, and methane are known from the earliest history but the chemical formula or reactions of the said molecules are still unknown. With the progress in chemistry, about the beginning of the eighteenth century, Lemery (1675) published a famous science journal, Cours de Chemie. It divided the chemical substances from natural sources into three classes,
- Substances come from minerals.
- Substances come from green plants.
- Substances come from animals.
History of organic chemistry
Lavoisier contribution to organic chemistry
Lemery's definition of organic compounds is accepted but very quickly Lavoisier (1784) provides new information for the classification of organic compounds or molecules on the basis of their sources. All compounds obtained from green plants and animal sources always contain carbon and hydrogen atom, and frequently, nitrogen, oxygen, and phosphorus. Lavoisier also showing the close relationship between green plants and animal products. With the improvement of the analytical chemistry, the organic substances are reclassification into two classes,
- Substances come from living organisms. Proteins, amino acids, enzymes, sugar, starch are examples of such types of organic compounds.
- Substances are made from non-living worlds.
Friedrich Wöhler contribution to organic chemistry
Chemical science goes step by step by the scope of new information, changing definitions or classifications, and production of the new substance or molecule in chemistry.
In 1828 Friedrich Wöhler converted ammonium cyanate into urea, a substance obtained from animal sources. It changes the definition and classification of organic chemicals.
The previous definition of organic molecule completely ended with the synthesis of acetic acid from its component chemical elements by Kolbe in 1845. Therefore, organic chemistry is the study of structure, properties, synthesis, and reactions of hydrocarbon or derivatives of hydrocarbon.
Classification of organic compounds
The number of organic compounds discovered at present has been estimated to be more than three million. It is impossible for a person to remember the name and chemistry of such a large number of organic compounds. But the scientific classification of such a large number of organic compounds into a small number of families on the basis of structure made it relatively simple and easy. Organic compounds are classified into three main groups depending on the nature of carbon chains.
- Acyclic compounds or aliphatic compounds
- Carbocyclic compounds
- Heterocyclic compounds
Aliphatic compounds
Organic compound processing open chin carbon atoms is called open chin or acyclic or aliphatic compound. The name aliphatic comes from the Greek word aleiphatos meaning fat. Fats have contained open chin structures. Therefore, open chin compounds are called aliphatic compounds. Some examples, names, and formulas of common open-chain organic compounds are given below the table,
| Functional group name | Class of organic compound | Example | Formula |
| Carbon-carbon single bond | Paraffin | ethane | CH3-CH3 |
| Alkane | ethane | ||
| Carbon-carbon double bond | Olefin | ethylene | CH2=CH2 |
| Alkene | ethene | ||
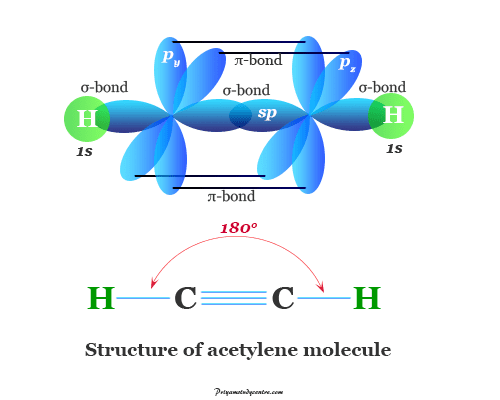
| Carbon-carbon triple bond | Acetylene | acetylene | CHΞCH |
| Alkyne | ethyne | ||
| Halo | Alkyl halide | methyl chloride | CH3Cl |
| haloalkane | chloromethane | ||
| Hydroxyl | Alcohol | methyl alcohol | CH3OH |
| Alkanol | methanol | ||
| Ether linkage | Ether | methyl ether | (CH3)2O |
| Alkoxyalkane | methoxymethane | ||
| Aldehyde or oxo or formyl | Aldehyde | formaldehyde | HCHO |
| Alkanal | methanal | ||
| Keto or oxo | Ketone | acetone | (CH3)2CO |
| Alkanone | propanone | ||
| Carboxyl | Carboxylic acid | formic acid | HCOOH |
| Alkanoic acid | methanolic acid |
Carbocyclic compounds
A large number of organic compounds which possess rings consisting of carbon atoms only are called carbocyclic compounds. These carbocyclic compounds are classified into three categories,
- Alicyclic compounds
- Aromatic compounds
- Non-benzenoid aromatic compounds
Alicyclic compounds
Alicyclic compounds are the class of organic compounds that behaves like aliphatic compounds. Cycloalkanes, cycloalkenes, and cycloalkynes are common examples of alicyclic organic compounds or hydrocarbons.
Aromatic compounds
Aromatic compounds are the class of organic compounds that possess benzene rings with a characteristic smell. The name aromatic comes from the Latin word aroma meaning odour. Some common examples of aromatic compounds are benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, chlorobenzene, phenol, etc.
Non-benzenoid aromatic compounds
Non-benzenoid aromatic compounds are the class of organic compounds that do not contain a benzenoid ring but have an aromatic character. Cyclopropenyl hexachloroantimonate, tetraphenyl chlorobutane fluoroborate, potassium cyclopentadienide are the example of non-benzenoid aromatic compounds.
Heterocyclic compounds
Heterocyclic compounds are the class of organic compounds that contain a ring with carbon and other elements commonly oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. There is a number of heterocyclic rings that are easily opened and do not possess any aromatic properties. For example, ethylene oxide, γ, or δ-lactone. These are not considered heterocyclic compounds. Heterocyclic organic compounds have five or six-membered heterocyclic rings which are stable. It contains conjugated double bonds. The rings exhibit aromatic character. Furan, thiophene, pyrrole, pyridine are common examples of heterocyclic organic compounds.
Give Classification of Organic Compounds With Example
Source: https://www.priyamstudycentre.com/chemistry/organic-compound
0 Response to "Give Classification of Organic Compounds With Example"
Post a Comment